Business Insights, HR and Payroll Tips and How-To
SSS Contributions: A Guide for Employees and HR Teams
13 Feb

The SSS Contribution is a vital aspect of employee welfare in the Philippines, ensuring access to social security benefits. Employees are required to contribute a percentage of their monthly salary to the Social Security System (SSS), which is matched by employer contributions. Understanding the intricacies of SSS Contributions is essential for both employees and HR teams to facilitate compliance and optimize benefits.
When people hear the term “SSS employee contribution,” they often assume it only concerns the employee. In reality, SSS employee contributions are a shared responsibility, and most of the accountability falls on the employer.
For HR and payroll teams, managing SSS contributions is not just about salary deductions. It involves correct computation, accurate records, timely remittance, and compliance with SSS regulations. A single mistake can affect employee benefits, trigger penalties, or cause problems during audits.
This guide focuses on what “SSS employee” means in payroll, how contributions are shared, common employer mistakes, and how companies can reduce compliance risks.
What “SSS Employee” Really Means in Payroll
In payroll operations, an “SSS employee” refers to an employee who is covered by the Social Security System and whose compensation is subject to mandatory SSS contributions.
From an HR and payroll perspective, this means:
- The employee’s salary must be evaluated based on SSS contribution rules
- A portion of the contribution is deducted from the employee’s pay
- The employer must add its required share
- The total contribution must be remitted to SSS on time
Once an employee is covered, SSS contributions are not optional. They must be included in every applicable payroll cycle as long as the employee remains employed and compensated.
Employer vs Employee Share of SSS Contributions
SSS contributions are divided between the employee and the employer. While the employee contributes through salary deductions, the employer plays a bigger role in the process.
Employee Share
The employee’s share is:
- Deducted directly from their salary
- Reflected clearly on the payslip
- Based on the employee’s compensation level under SSS guidelines
Employees rely on employers to ensure their deductions are correct and properly remitted.
Employer Share
The employer is responsible for:
- Paying its share of the SSS contribution
- Covering the Employee Compensation (EC), which is employer-paid
- Computing the correct total contribution
- Remitting the full amount (employee + employer share) to SSS
Important note: SSS contribution amounts are based on official SSS contribution schedules, which may change. Employers should always follow the latest SSS-issued contribution table.
Why Accuracy in SSS Contributions Matters
SSS contributions directly affect:
- Employee eligibility for loans and benefits
- Retirement, sickness, maternity, and disability claims
- Employer compliance standing with SSS
Incorrect or delayed contributions can result in denied employee claims, disputes, and penalties for the employer.
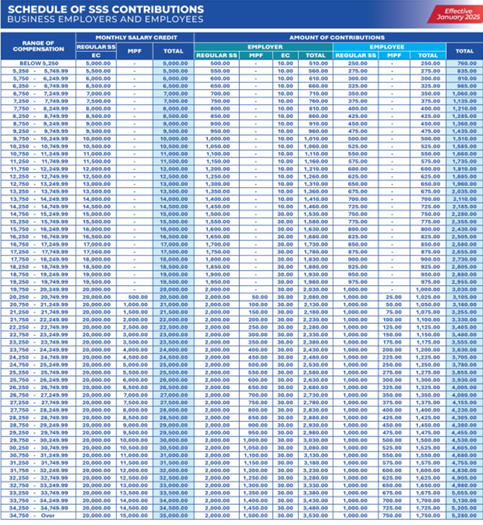
Common Mistakes Employers Make with SSS Contributions
Even with experience, HR and payroll teams can encounter issues. The most common mistakes include:
Using Outdated Contribution Tables
SSS updates contribution schedules from time to time. Using old tables can result in underpayment or overpayment.
Incorrect Salary Classification
Errors in salary reporting can lead to incorrect contribution computation, affecting both employer and employee shares.
Late or Missed Remittance
Even if payroll deductions are correct, late remittance can still result in penalties and interest charges.
Employee Record Errors
Incorrect SSS numbers, misspelled names, or mismatched personal details can cause contributions to be unposted or misapplied.
Over-Reliance on Manual Payroll
Manual payroll processes increase the risk of calculation errors, missed updates, and inconsistent records.
These issues can accumulate over time and create compliance gaps.
Penalties for Incorrect or Late SSS Remittance
SSS strictly enforces employer compliance. Failure to remit correct contributions on time may result in:
- Penalties for late payment
- Interest charges on unpaid contributions
- Issues during SSS audits
- Delays or denial of employee benefit claims
- Possible legal consequences for repeated violations
Beyond financial penalties, non-compliance can damage employee trust and company reputation.
How HR Teams Can Reduce SSS Compliance Risks
To manage SSS contributions effectively, HR teams need structured processes and accurate data. Best practices include:
- Regularly reviewing SSS guidelines and updates
- Verifying employee SSS details during onboarding
- Conducting payroll checks before remittance
- Keeping clear records of contributions and remittances
As the workforce grows, manual tracking becomes harder to maintain consistently.
How HR Systems Help Ensure SSS Compliance
HRIS and Payroll systems help address many of the challenges associated with SSS contributions.
These systems can:
- Automate SSS contribution calculations based on salary data
- Reduce errors caused by manual computation
- Maintain consistent employee records
- Generate payroll and contribution reports
- Support timely and accurate remittance
By centralizing payroll and employee information, HR teams gain better control and visibility over compliance-related tasks.
Supporting Payroll Compliance with HRIS and Payroll Solutions
Using an integrated HRIS and Payroll system helps businesses manage SSS contributions more efficiently and securely.
With solutions like Decode Technologies’ HRIS and Payroll System, companies can:
- Ensure accurate payroll computations
- Reduce compliance risks related to SSS
- Maintain organized employee contribution records
- Improve payroll transparency for employees
Instead of spending time correcting errors, HR teams can focus on operational efficiency and employee support.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Are SSS contributions mandatory for employees?
Yes. Employees covered by SSS are subject to mandatory contributions as long as they are employed and receiving compensation.
Who is responsible for remitting SSS contributions?
The employer is responsible for computing, deducting, and remitting both the employee and employer shares to SSS.
Can incorrect SSS contributions affect employee benefits?
Yes. Incorrect or missing contributions can delay or deny employee benefit claims.
Do SSS contribution rates change?
SSS contribution schedules may be updated. Employers should always refer to the latest official SSS guidelines.
How can companies minimize SSS payroll errors?
Using an HRIS and Payroll system helps automate calculations, reduce manual errors, and maintain accurate records.
Recent Posts
- PhilHealth Online Registration: A Guide for New Employees and Employers February 24, 2026
- Pag-IBIG MP2: How Employers Can Support Employee Savings Programs Through Payroll System February 20, 2026
- 2026 People Power Revolution Holiday: What Employers Need to Know About Pay Rules February 19, 2026
- SSS Contributions: A Guide for Employees and HR Teams February 13, 2026
- Virtual Pag-IBIG: What Employers and Employees Need to Know in the Philippines February 10, 2026